Jinqiang Zhang's group has made important progress in antibacterial stapled peptides
In March 2020, Jinqiang Zhang's group published a research paper entitled ‘Novel Stapling by Lysine Tethering Provides Stable and Low Hemolytic Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides’ in Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
The widespread problem of bacterial multidrug resistance makes it urgent to develop novel antibiotics. The discovery of penicillin marked the beginning of human research on anti-bacterial infection drugs. However, drug-resistant strains have been found in the marketed antibiotics in a very short time. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find novel treatments to deal with infections caused by these resistant bacteria.
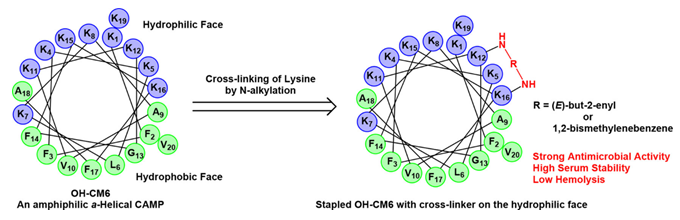
Based on this, Hong Li,Associate Professor Zhang Jinqiang's group, school of Pharmaceutical science, Chongqing University,developed a novel type of cationic bridged antimicrobial peptide with good broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. The author successfully developed a novel cationic bridging staple peptide synthesis method, using the N-alkylation reaction of the ε-amino group of lysine on the hydrophilic surface of cationic antibacterial peptide, connecting two amino groups through the alkyl chain to form a staple structure. Based on this method, using the antimicrobial peptide OH-CM6 as a template, a series of cationic bridged antimicrobial peptides with a staple structure introduced on the hydrophilic side of the antimicrobial peptide were synthesized. The antimicrobial activity, protease stability, hemolytic toxicity and cytotoxicity were screened, and two cationic bridged antimicrobial peptides with high antibacterial activity, good protease stability, and low hemolytic toxicity were obtained. It was found that cationic bridging peptide 12 had a strong lysis effect on bacterial cell membrane, so it could kill bacteria quickly.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21602024) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (project no. 2018CDYXYX0027).
View Article Online: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02025