The medicinal chemical biology group reports a new approach to drug discovery in Nature Chemistry
On December 21, 2020, a team from Chongqing University, in collaboration with the University of Hong Kong and Naval Medical University, published a paper entitled "Selection of DNA-encoded chemical libraries against endogenous membrane proteins on live cells" in Nature Chemistry. Professor Yizhou Li from Chongqing University, Professor Xiaoyu Li from the University of Hong Kong and Professor Yan Cao from Naval Medical University are the co-authors of the paper. This is the second time in recent years that a team from the School of Pharmaceutical Science of Chongqing University has published representative research results in this journal (link to related work: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-018-0017-8).
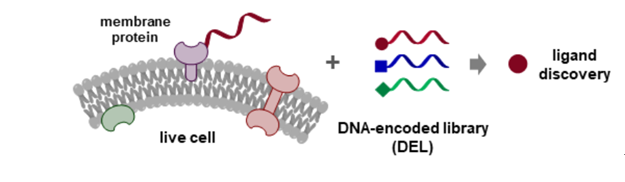
Based on the accumulated research in DNA-Encoded Chemical Libraries (DEL) technology, the joint research team has developed a new method for drug discovery targeting membrane proteins: "precise tracing" of membrane proteins in the complex physiological environment of living cells through specific DNA probes. This technique can be used to obtain active compounds against the GPCR superfamily, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and other “hard to druggable” targets.
Yizhou Li and Xiaoyu Li jointly proposed the new method for the drug discovery and led the completion of the research work. Postgraduates Qigui Nie and Shilian Yang from School of Pharmaceutical Science of Chongqing University, and undergraduate student Cen Huang (who has gone to Hong Kong University for his PhD) participated in and completed some of the experimental work.
Link to the paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-020-00605-x
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-020-00605-x.